The internet often feels like a barrage of VPN advertisements. I speak from experience, having immersed myself in writing VPN content and conducting thorough research for the past month. However, it’s essential to emphasize their significance. We’re not here to overstate the point but to highlight that VPNs are invaluable tools that provide online safety and privacy at a reasonable monthly cost.
Yet, delving deeper into the realm of VPNs can be perplexing. What exactly is DNS? How do IP addresses function? A tunnel? What does that entail? These are common queries we’ve encountered—questions that have prompted me to ponder and stroke my beard in contemplation. Additionally, inquiries such as “Are VPNs secure?” arise.
Undeniably, newcomers to the VPN world might be curious about why and how to utilize one. The technical jargon surrounding VPNs can make them appear daunting to those seeking an added layer of online security. Therefore, here’s a comprehensive guide to understanding VPNs, providing you with the necessary knowledge to confidently navigate this terrain.
VPN Meaning
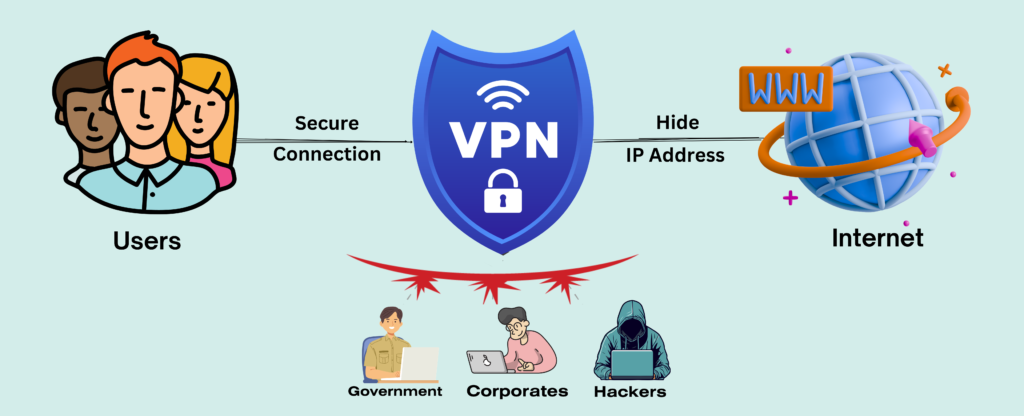
A Virtual Private Network establishes a protected connection between your system (such as a smartphone or laptop) and the internet. This connection shields your identity and online activities from your ISP, government agencies, and potential hackers.
Your device continuously exchanges data with various parties online when you’re using the internet.
Without realizing it, you often grant websites access to your IP address (which discloses your precise location) and details like your browsing history, operating system information, device identifiers, and much more.
VPN Encryption
VPNs rely on encryption to enhance the security and privacy of internet users. A VPN’s functionality centers around encryption, a method that conceals the true meaning of data. This means that data remains indecipherable unless someone possesses the corresponding password, known as an encryption key. When you employ a VPN, the encryption key safeguarding your data and online activities is exclusively known to your computer and the VPN server.
Point-to-Point Tunneling Protocol (PPTP)
PPTP, developed by Microsoft, is one of the oldest active protocols on the internet. It utilizes the Transmission Control Protocol (TCP) control channel and the Generic Routing Encapsulation (GRE) tunneling protocol.
PPTP relies on the Point-to-Point Protocol (PPP) for security features, establishing a direct Layer 2 communication protocol between two routers.
Layer 2 Tunneling Protocol
This protocol incorporates PPTP with the Layer 2 Forwarding (L2F) tunneling protocol, reinforcing the data tunnel provided by PPTP. However, L2TP itself does not offer encryption or privacy capabilities.
Secure Socket Tunneling Protocol (SSTP)
SSTP, created by Microsoft, is a notably secure VPN tunneling option. It transports PPP traffic via the Secure Sockets Layer (SSL) or Transport Layer Security (TLS) channel, ensuring encryption, key negotiation, and traffic integrity checks.
Internet Key Exchange Version 2 (IKEv2)
IKEv2 manages request and response actions to guarantee secure and authenticated traffic, commonly using IPsec. Supporting 256-bit encryption allows the usage of famous ciphers such as Advanced Encryption Standard (AES), Camellia, and ChaCha20. IKEv2 is primarily employed to secure mobile devices, where it proves particularly effective.
OpenVPN
Widely recognized as the premier open-source VPN technology, OpenVPN employs pre-shared certificates, secret keys, usernames, and passwords to authenticate every device or server.
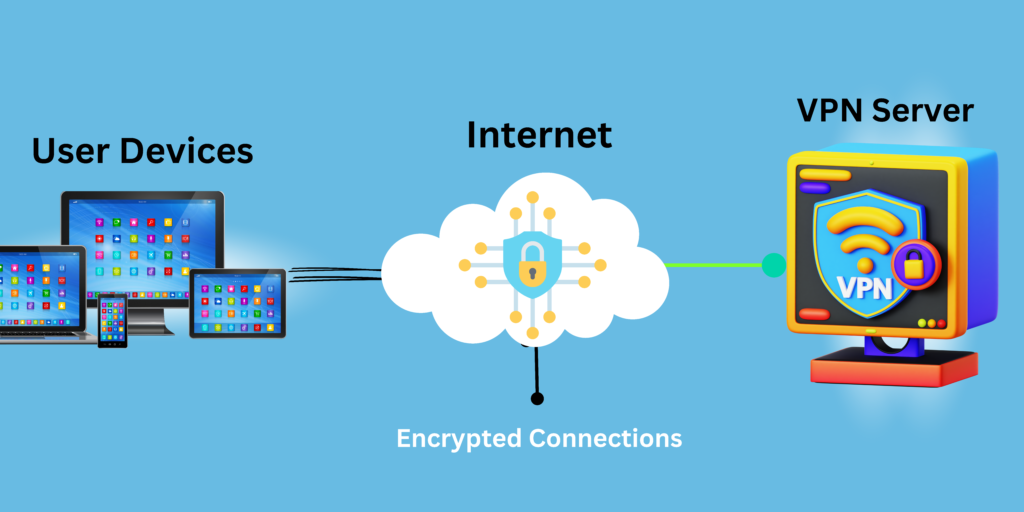
How does a VPN work?
A VPN operates by rerouting all the data from your laptop or phone before it reaches the Internet, rather than sending it directly through your Internet Service Provider (ISP).
When you use a VPN, it initiates data encryption on the client side. Once the data is encrypted, it is channeled through a secure VPN tunnel inaccessible to others, and from there, it proceeds to the internet.
Before passing through the VPN tunnel, your request goes to your ISP. However, since it’s encrypted, the ISP cannot discern what you’re attempting to access. Instead, it forwards your request to your VPN server. Subsequently, it dispatches the request to the intended IP address or website.
Why use a VPN?
Security
With VPNs, your internet traffic is encrypted, making it challenging for others to monitor your online activities. This is critical while utilizing public Wi-Fi networks, which are typically insecure and prone to hackers.
Privacy
It safeguards your privacy by hiding your IP address and preventing websites, advertising, and government agencies from tracking your online activity. Increases online privacy and anonymity.
Access Control
VPNs route connections through servers in other countries to access geo-restricted content and websites. This can help you access prohibited streaming services, news sites, and other websites.
Bypassing Censorship
They can unlock the internet in nations with tight internet control.
Business and Remote Work
Businesses and remote workers need VPNs to access critical data from anywhere in the world securely.
VPNs Questions & Answers
What is VPN configuration?
A VPN configuration is setting up a new Virtual Private Network connection on a device or router. Performance- and security-related settings must be chosen to get an ideal private surfing experience with your existing internet service provider.
How to set up a VPN?
- Get a VPN program from the Windows Store or online.
- Go to “Settings” and select “Network” before selecting “VPN.”
- The entries for “Server Name,” “VPN Type,” and your account information must be shared by the VPN service you selected. Then click “Add a VPN.”
- Save your VPN
How much does a VPN cost?
In broad terms, a monthly subscription typically costs around $10. However, the cost decreases considerably if you opt for a longer commitment, like a year or two.
How do you change the VPN location?
- Opt for a VPN with a wide range of server locations.
- Install the application on your device.
- Launch the app and sign in.
- Connect to a VPN server in a different country.
- Experience your virtual location!
Are VPNs secure?
While nothing on the internet can be guaranteed to be 100% secure, there will always be methods to breach services like VPNs. Nonetheless, in most cases, it will offer more benefits than risks.
What do zero logs mean?
We provide a VPN service with zero logs. This implies that we don’t record your internet activities—nothing to keep or show anyone, and nothing to share.
What is smart DNS?
Using your DNS to unblock geo-restricted websites and services is the foundation of the Smart DNS. It resembles how proxy servers conceal your true IP address and location by routing your internet traffic through a faraway server.
















Pingback:SSL Certificates: Definition, Explanation & Types | Renewcoupons
Pingback:Avast VPN Vs CyberGhost- Best VPNs on The Market?
Pingback:Watch UFC Streaming Online With [5 Best VPNs] in 2023
Pingback:Avast Vs F-Secure- Who Wins The Battle?
Pingback:Best Free VPN for Android- Unlimited Downloads